Encrypting Root File System with Zymbit Security Modules

Prerequisites
Raspberry Pi:
- Raspberry PI OS: Bookworm (64 bit)
- Raspberry PI OS: Bullseye (32 or 64 bit)
- Raspberry PI OS: Buster (32 or 64 bit)
- Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (32 or 64 bit)
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (32 or 64 bit)
- Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (32 or 64 bit)
BACKGROUND
To skip the background information and start encrypting your RFS, click here.
WHY ENCRYPT?
There are many reasons to encrypt the Root File System (RFS), from keeping WiFi credentials immutable to keeping proprietary software and sensitive data from being cloned.
For most Raspberry Pi configurations, only two partitions exist:
- /boot on /dev/mmcblk0p1
- / on /dev/mmcblk0p2
INTRODUCING LUKS
LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup) is the popular key management setup for dm-crypt, the de-facto standard for block device encryption with Linux.
LUKS provides a robust and flexible mechanism for multiple users (and services) to interface to and access Linux’s ‘dm-crypt’ infrastructure.
dm-crypt is a transparent disk encryption subsystem in Linux kernel versions 2.6 and later and is part of the device mapper infrastructure, and uses cryptographic routines from the kernel’s Crypto API. Both are widely used and understood in the IT community.
Weaknesses of single Master key
dm-crypt has a single Master Key that is used to encrypt / decrypt data in/out of the block. To ensure long term security and deal with changing authorized users/services, it would be necessary to change the Master Key frequently, and potentially share it with multiple users/services on a regular basis. Every new iteration of Master Key would require the underlying data block to be re-encrypted everytime. In real systems, touched by different users/services, this is impractical.
Hierarchical key management
A more practical solution is to have a hierarchical key management setup in which users/services are given User Keys that are used to release the MasterKey. User Keys can be easily changed and revoked, without having to re-encrypt the underlying data block. The management of such a hirearchical key managers is the role of LUKS.
In this post we show how to use Zymbit Security Module to lock a User Key, that is subsequently used to unlock the Master Key and provide access to the Root File System. If you’d like to learn more about LUKS see the References at the bottom of this post.

SECURE STORAGE OF LUKS USER KEYS
The security efficacy of your LUKS encrypted RFS is highly dependent upon how the User Keys are generated and where they are stored.
The SD Card is NOT a secure storage location
The growing single board computer family is awesome, and we love it! It is inexpensive, has an incredible amount of computing power for an embedded device and has a very robust software development ecosystem.
However, these devices have an Achilles heel: the SD card is the primary software deployment media, and it can be very easily removed and manipulated.
The natural inclination would be to encrypt the file system using LUKS on dm-crypt, but for unattended use across many deployed units the obvious question is: where is the LUKS key stored? Of course, it’s the file system. Even if you try to obfuscate it through various programmatic means, the key is still very vulnerable to attack.
Securing LUKS User Key with Zymbit Security Module.

The Zymbit Security Module provides a general “locking” service whereby a block of plaintext data is encrypted and signed.
When used with LUKS, the User Key is sent to the Zymbit Security Module to be locked (encrypted and signed) when the file system is created. When the system boots and needs to decrypt the root file system, the locked LUKS key is “unlocked” (signature verified and contents decrypted) and presented to dm-crypt. If the key was unlocked successfully, the boot process continues normally. Here is the boot sequence with a LUKS/dm-crypt filesystem where the key is protected by Zymbit Security Module:
- The kernel initializes initramfs
- initramfs presents the locked LUKS key to Zymbit Security Module
- Zymbit Security Module validates the signature and decrypts the key*
- The decrypted key is presented to LUKS and the root file system is then decrypted
*requires that Zymbit Security Module operational status is “secure”
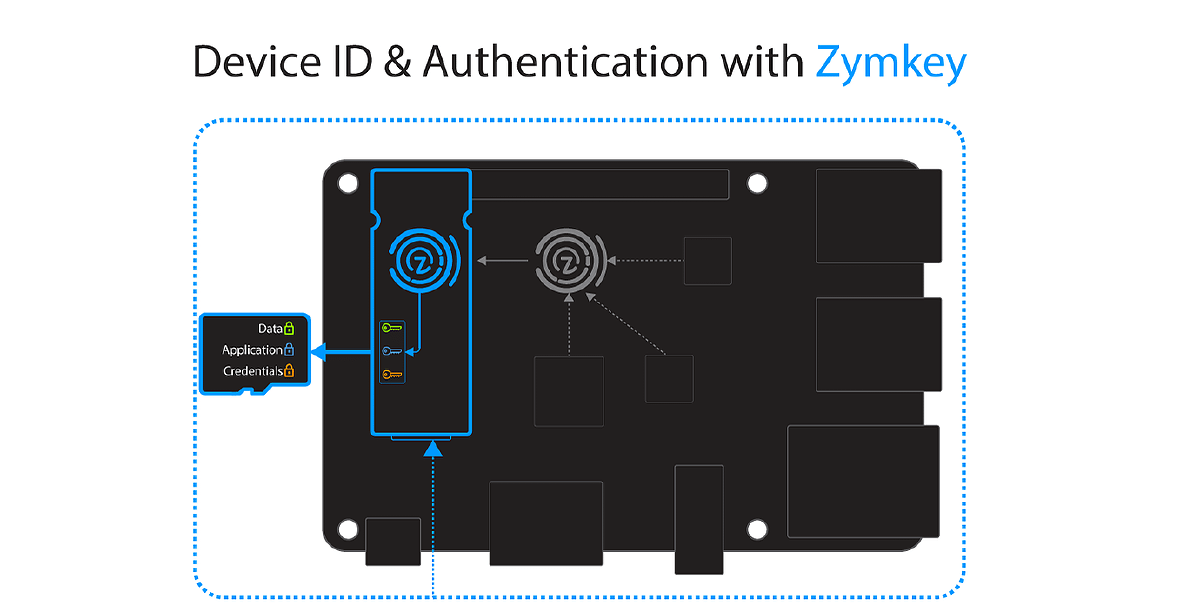
ZYMKEY4 fitted to Raspberry Pi

Zymbit Security Module Authenticates Host System Before Unlocking LUKS Key
One of the key features of Zymbit Security Module is to generate a unique Identity (ID) for the host system, based upon a fingerprint that measures specific system components. This fingerprinting process is used to “bind” together a specific Zymbit Security Module (root of trust, key store, crypto services), a specific host computer and a specific SD card. Once bound, these components form a permanent and immutable ID of the host system.
Each time the host device boots, and at random intervals thereafter, the Zymbit Security Module rechecks the ID fingerprint. If any of the system components have changed the fingerprint changes and the system is deemed to have been compromised, authentication fails and all security services are shut down.
Using this ID / Authentication feature, the Zymbit Security Module can be used to protect LUKS User Keys in unattended applications, where it might be easy to remove and copy SD card content. (The Zymbit Security Module also has other physical security features which are also used to lock/enable security services)
WHERE TO STORE YOUR LUKS ENCRYPTED RFS
LUKS is very versatile and can be applied to both SD Card and external storage media. Lets review the pros and cons of each option:
When encrypting your rootfs, we highly recommend turning off unattended-upgrades prior to the encryption process. In some cases primarily with Ubuntu, during an update/upgrade after encryption, the update-initramfs process may fail and leave the system unable to boot.
To mitigate this issue, remove the service unattended-upgrades:
systemctl stop unattended-upgrades
systemctl disable unattended-upgrades
apt remove unattended-upgrades -y
Option 1 - Convert existing SD Card to LUKS
Converting the existing root file system on the SD card still requires an external device (e.g. USB flash drive) that is used as a temporary boot root file system: this provide an easier and lower risk means to convert and copy the original contents. The external devices needs to be a little larger than the existing root file system in order to store the old file system.
Pros:
- Less physical space requirements.
- Much less power required.
Cons:
- Conversion is more complex and time consuming than migrating to an external drive.
- Data space constraints.
- Write cycle constraints.
- Access speed constraints.
Process Steps Run By Script:
- Make a tarball of the original root file system and store it on the external device
- Copy the original root file system files to the external device to form a temporary file system
- Boot to the temporary file system. Once booted, the temporary file system will:
- Create a LUKS key
- Lock the LUKS key with Zymbit Security Module
- Create a LUKS volume on the original root partition.
- Create an ext4 partition on the LUKS volume on the original root partition
- Untar the root file system tarball into the converted partition
Option 2 - Migrate existing SD card to external LUKS storage device.
The existing root file system can be migrated to an external LUKS encrypted USB flash, hard drive or SSD.
Pros:
- External devices can hold much more data.
- Migration is easier and quicker than SD card conversion method.
- Some external devices have much faster data access than SD cards.
- Some external devices (e.g. HDD) can tolerate many more write cycles than an SD card.
Cons:
- For HDD and SSD and non-compact USB flash devices, there are additional power requirements.
- Except for compact USB flash devices, physical space requirements also increase. This may be especially important for the Raspberry Pi Zero family.
Process Steps Run By Script:
- Create the LUKS key
- Lock the LUKS key
- Create a LUKS volume on an external USB device
- Create an ext4 partition on the LUKS volume
- Move the existing root file system to the LUKS volume on the external device
- Boot to the new root file system and erase the previous root volume
HOW TO ENCRYPT
BUILDING YOUR LUKS ENCRYPTED RFS
Prerequisites
- Follow the Installation and Getting Started section for your HSM first.
Option 1 - Convert existing SD Card to LUKS
To convert your root file system to LUKS/dm-crypt, you will need to connect an external USB disk (as temporary storage). As mentioned previously, this is necessary because it is not possible to encrypt the partition in place, so the external disk is needed as temporary storage and a temporary root file system while the conversion takes place. The external disk needs to be at least twice as big as the root partition. Next, run the following script:
curl -G https://s3.amazonaws.com/zk-sw-repo/mk_encr_sd_rfs.sh | sudo bash
For RPi users: This script is parameterized, so if you have special requirements (e.g. root file system lives on /dev/mmcblk0p4), you can invoke it in the following fashion:
curl -G https://s3.amazonaws.com/zk-sw-repo/mk_encr_sd_rfs.sh | sudo bash -s -- -x <path to external storage device (e.g. /dev/sdX> -m <source partition number>
In the above invocation with no parameters, the defaults are:
- Original root file system located on /dev/mmcblk0p2
- Temporary root file system/storage for original root tarball located on /dev/sda
- Temporary root file system takes up entirety of new device
The very first run of this script on a new temporary external USB disk could take a long time. Also, two reboots are required before the script is complete.
One thing to note is that, if the external storage device has an ext4 formatted partition with the original root file system partition (e.g. /dev/mmcblk0p2) on it, this script will use what is already on the external storage device to convert the SD card. This cuts down time for converting lots of device root file systems and allows the script to be used in a mass production deployment.
On a Pi4 with an attached USB SSD as the external device on a bare Bullseye “full” version, the first run of this script requires 30 minutes or so to complete the first phase. The second phase takes around 10 minutes.
Based on the above, using the formatted external device to convert subsequent units should only take around 10 minutes.
Option 2 - Migrate existing SD card to external LUKS storage device.
To migrate your root file system to an external USB device, you can run the following script:
curl -G https://s3.amazonaws.com/zk-sw-repo/mk_encr_ext_rfs.sh | sudo bash
This script is parameterized, so if you have special requirements, you can invoke in the following fashion:
curl -G https://s3.amazonaws.com/zk-sw-repo/mk_encr_ext_rfs.sh | sudo bash -s -- -x <path to external storage device (e.g. /dev/sdX> -p <destination partition number -s <max size of new root partition> -m <source partition number>
In the above invocation with no parameters, the defaults for RPi are:
- Original root file system located on /dev/mmcblk0p2
- New root file system located on /dev/sda1
- New root file system takes up entirety of new device
Please note that the new root file system should be at least a little larger in size than the original root partition
Running this script takes around 30-40 minutes. The Zymbit Security Module’s LED flashes rapidly until the process has completed.
INTEGRATING LUKS INTO VOLUME MANUFACTURING WORKFLOW
The examples above are designed to help you get up and running with single and low volume applications.
If you require support in developing a high volume manufacturing encryption workflow then please contact us to discuss our OEM engineering services.