HSM60: Compute Module Interposer - Quickstart and Integration
HSM60 Integration Guide
The Zymbit HSM60 is a security interposer designed to work with the Raspberry Pi CM4 or CM5 as a drop in HSM with the same form factor. It also can facilitate compute upgradeability, allowing a CM5 to be used on an IO board originally designed for a CM4.
Note: Although using a CM4 on an IO board for a CM5 is technically possible, this is not recommended nor supported by Zymbit.
This integration guide will walk you through how to install a Zymbit HSM60 Security Interposer onto a Raspberry Pi CM5 IO board with a Raspberry Pi Compute Module 5.
Hardware Installation
Mount Assembly
- Remove the compute module from the IO board
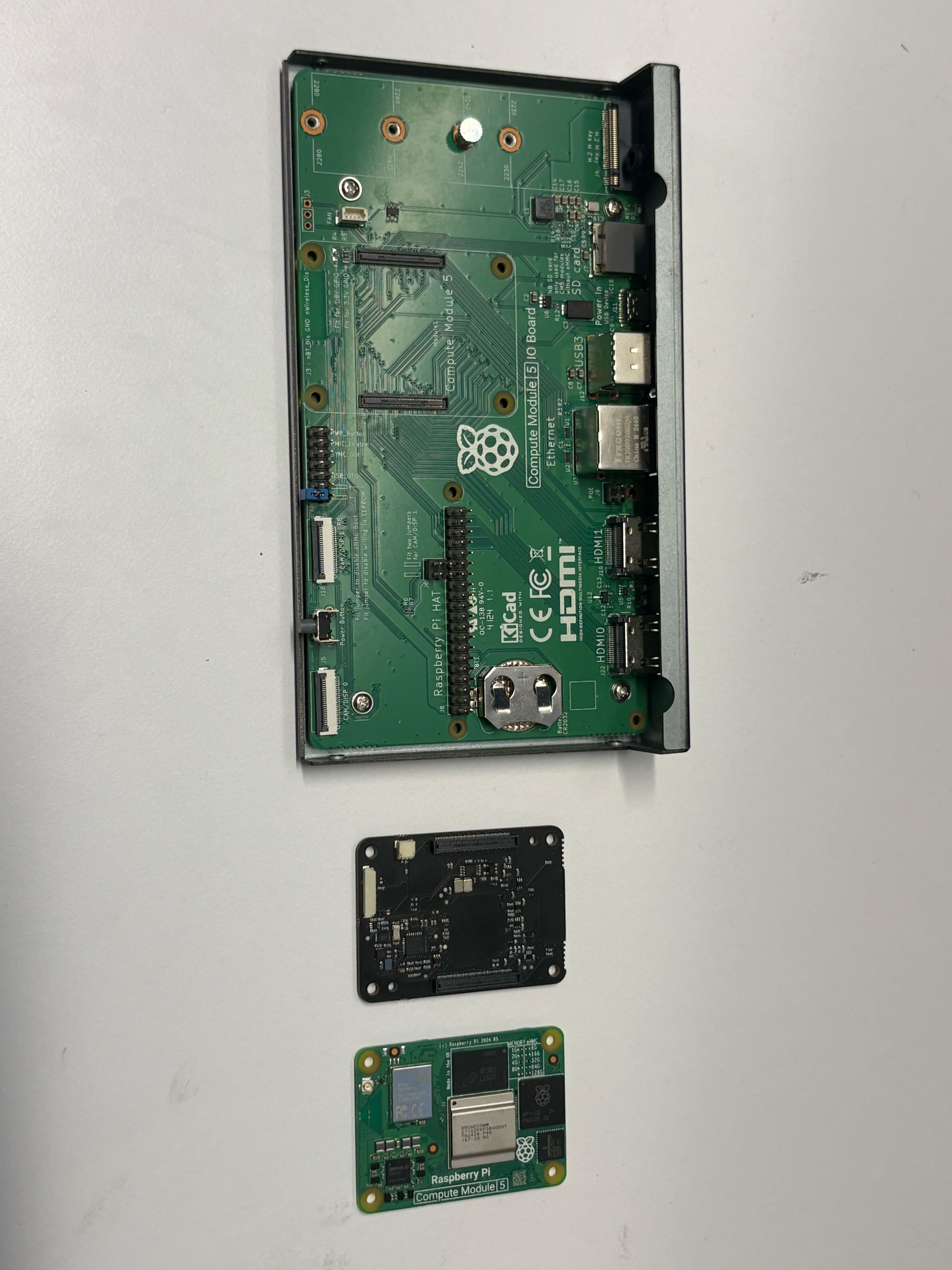

- Install the HSM60 onto the IO board ensuring that both connectors click in and it sits flat
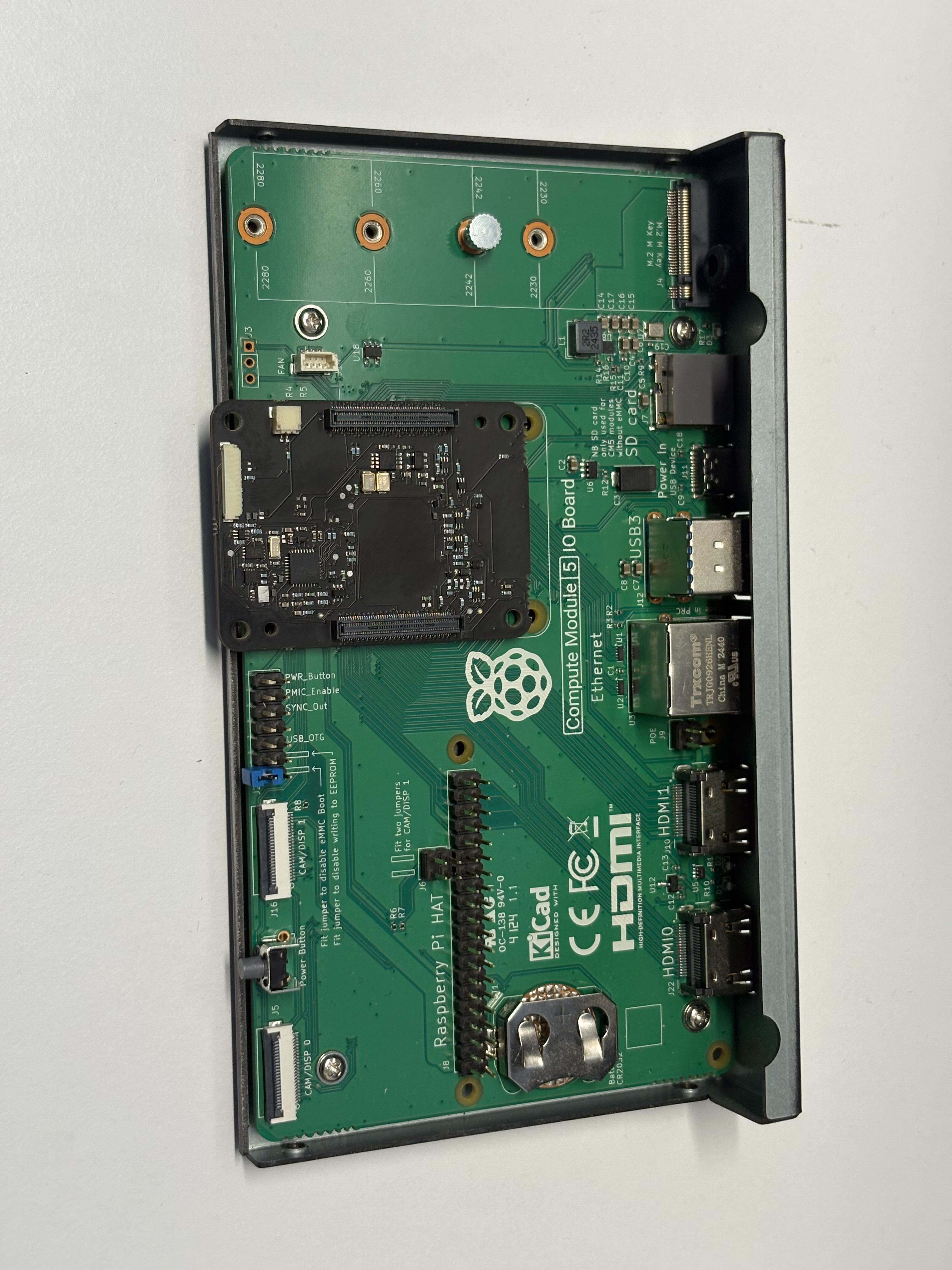


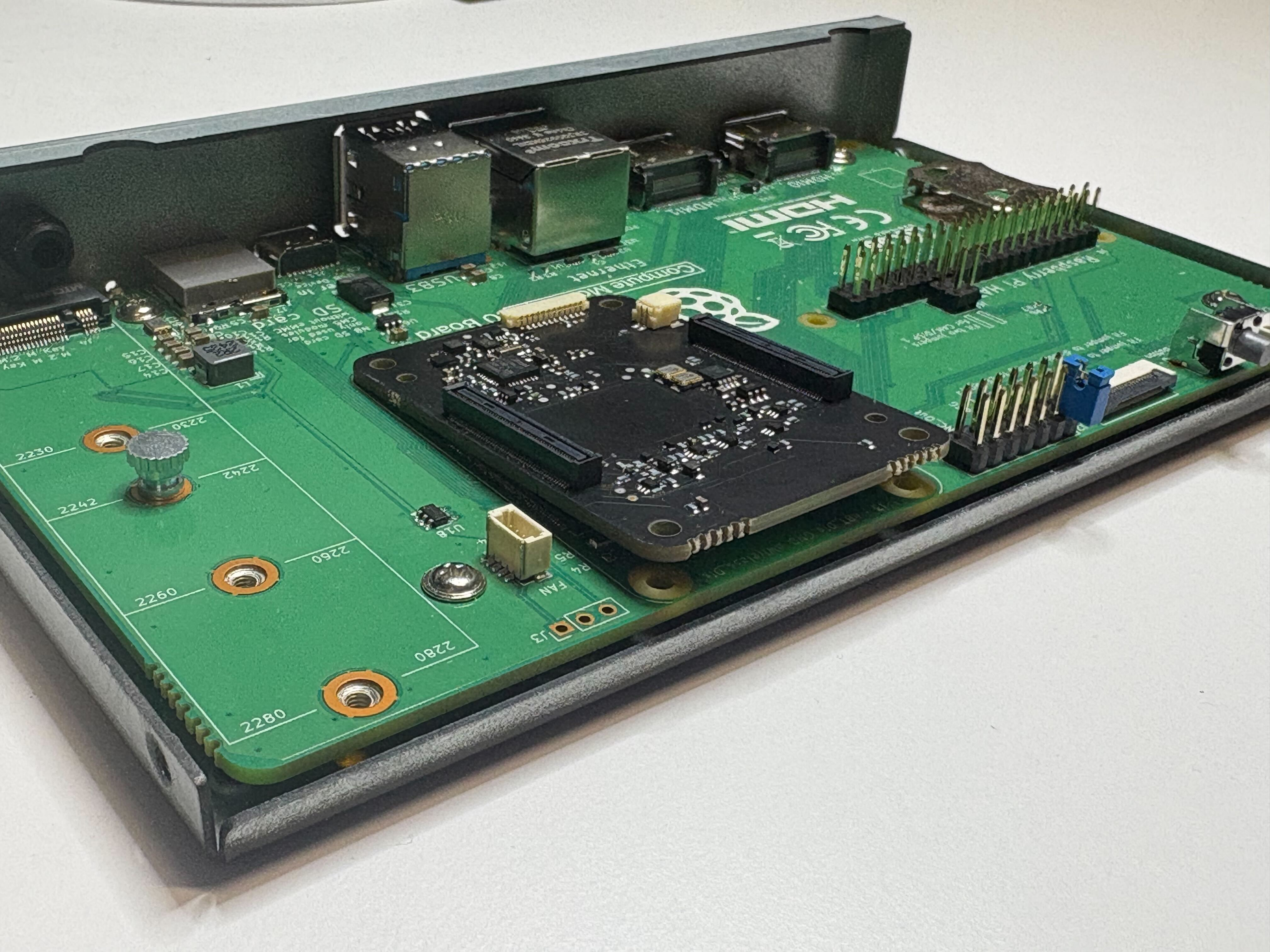

- Install the Raspberry Pi Compute Module
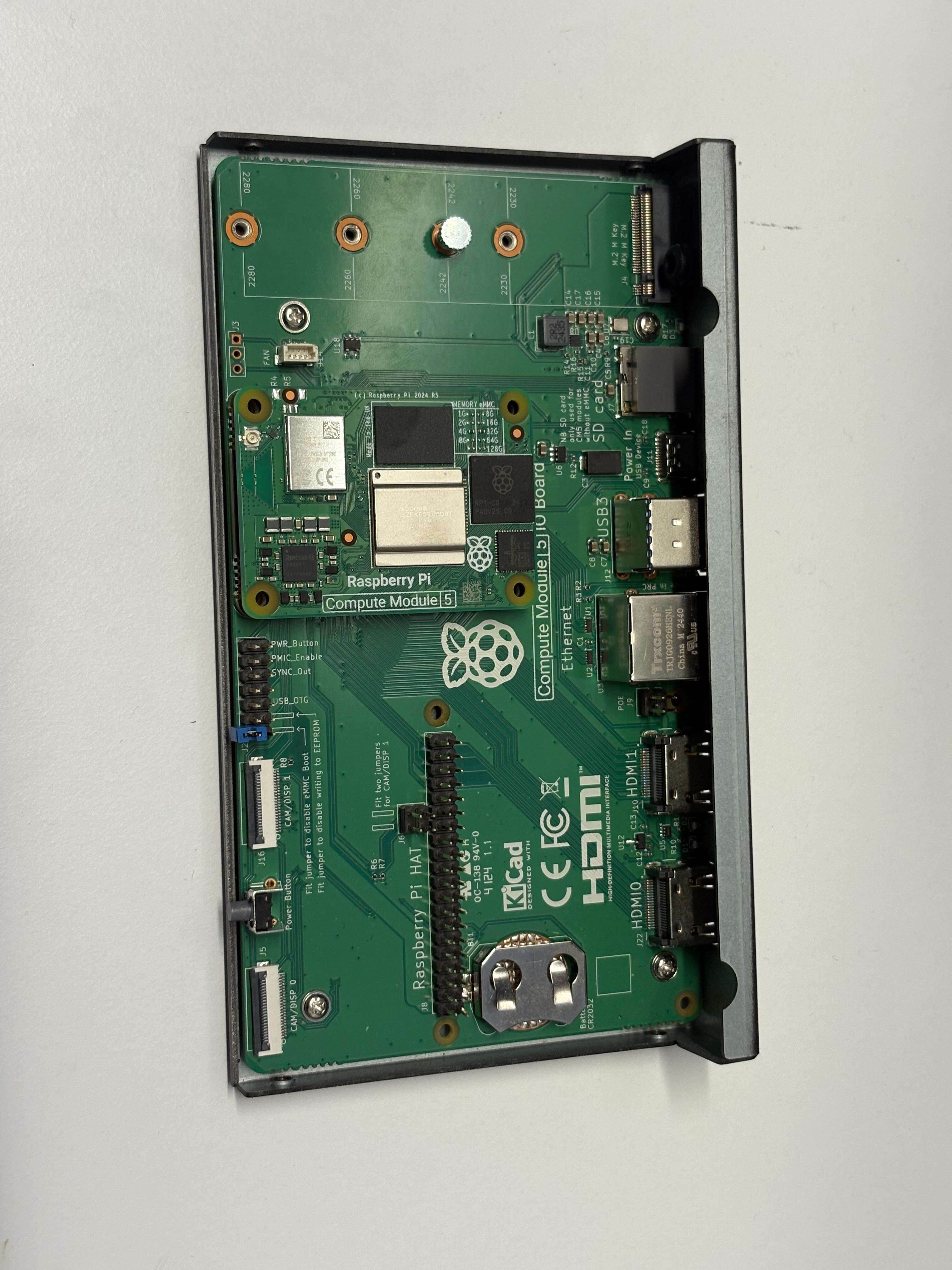

Software Installation
Overview:
- Enable the I2C bus in order to communicate with the HSM.
- Install the Zymbit Driver Package
- Test the installation
Establish an I2C connection
For Raspian-based operating systems, you must configure the state of the I2C.
- Log in to your Raspberry Pi and run
sudo raspi-config. - Navigate to Interfacing Options -> I2C -> Would you like the ARM I2C interface to be enabled?
- Select yes, and confirm this choice.
Your I2C bus is now configured and ready to talk to the HSM. The default I2C address for the HSM is 0x30.
Your I2C bus is now on and ready to talk to the HSM.
Install the Zymbit Driver Package
Login to your host device and follow these steps to install the HSM’s Zymbit Driver Package.
The HSM will require a number of packages to be installed from the Raspbian and Zymbit apt repositories. The following setup script will be install a number of files and software packages on your system, including:
- Zymbit
.servicefiles located in the/etc/systemd/systemdirectory pip3
Ensure that curl is installed on your host:
sudo apt install curl
Download and install the necessary Zymbit services onto your device.
curl -G https://s3.amazonaws.com/zk-sw-repo/install_zk_sw.sh | sudo bash
When the software installation has completed, the script will automatically reboot your device. After the reboot has completed, the Pi will perform an operation that will temporarily bind the HSM to your SBC. Once the HSM is bound to the SBC, the HSM’s blue LED should blink slowly–once every 3 seconds–to indicate that the binding is complete.
Test the installation
The quickest way to get started is to see the HSM’s various features at work by running these test scripts that were installed with the Zymbit Driver Package:
python3 /usr/local/share/zymkey/examples/zk_app_utils_test.py
python3 /usr/local/share/zymkey/examples/zk_crypto_test.py
Now you’re ready to start developing with HSM and Raspberry Pi, or install Bootware.
When it’s time to deploy your project, read our guide on enabling Production Mode:
Additional Hardware Configuration.
Battery Connector (J8)
The battery connector is a 1.00mm Pitch, 2-pin, JST PCB header that mates with housings with 02SR-3S or similar headers. This is the same battery connector that is on the Pi5. It takes 3.3V batteries (like the Pi5 battery) and is used to power the RTC on the ZYMBIT HSM as well as power the security supervisor on the HSM in a low-power state when there is no primary power. See API documentation for uses.
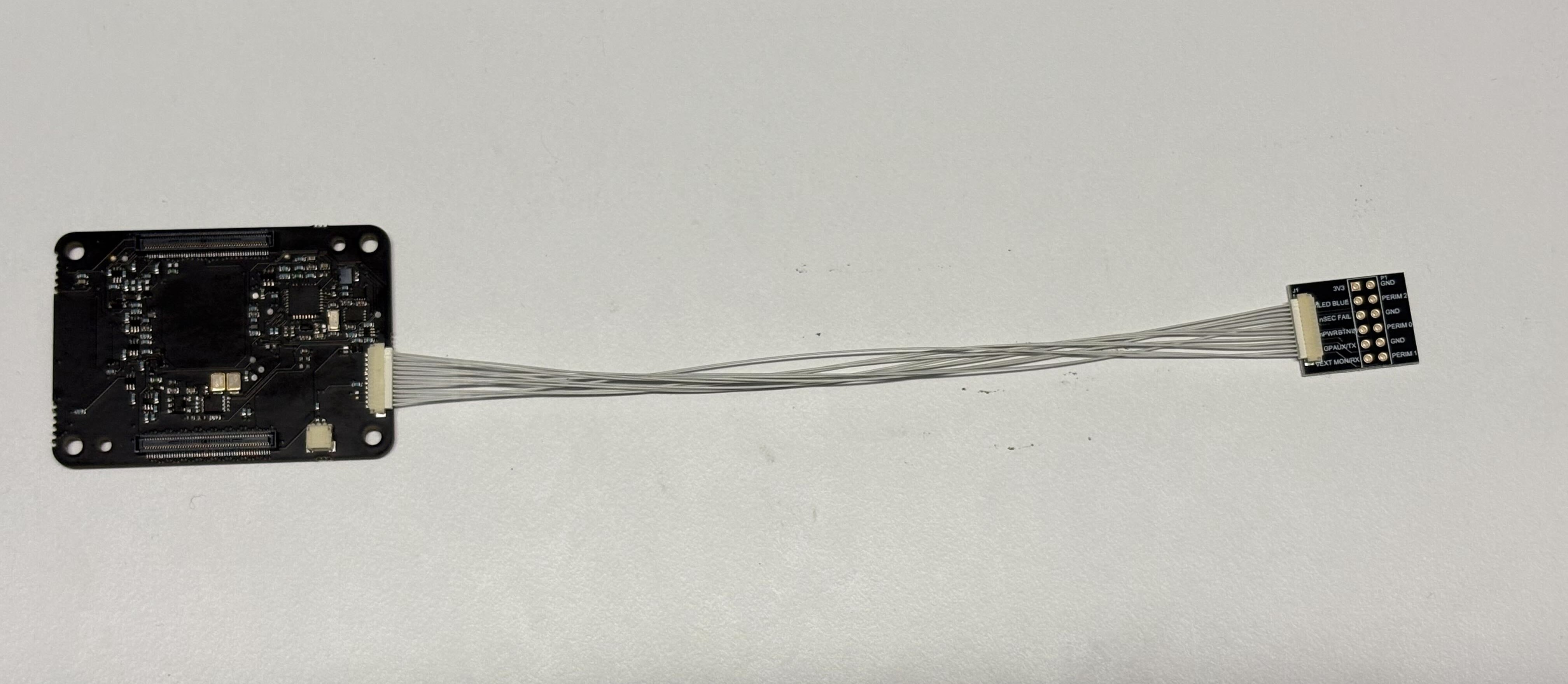
Auxiliary Connector (J1)
This connector is a 12 pin JST SURS connector (SM12B-SURS-TF(LF)(SN)) and mates with 12SUR-32S (premade cable harnesses)


| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PERIM_1 | Tamper detection loop 1 recieve |
| 2 | GND | System ground |
| 3 | PERIM_0 | Tamper detection transmit. Connect this pin to PERIM_1 and/or PERIM_2 |
| 4 | GPAUX_IN_RD/ | |
| VEXT_MON | General purpose auxiliary recieve (future use) and external voltage monitor pin (future use) | |
| 5 | PERIM_2 | Tamper detection loop 2 recieve |
| 6 | GPAUX_OUT_TXD | General purpose auxiliary transmit (future use) |
| 7 | RSVD_GND | Ground pin that is reserved for potential future use. |
| 8 | 3V3_CM4 | 3.3V output from the Raspberry Pi |
| 9 | nSECURE_FAIL | Zymbit security fault indicator |
| 10 | LED_C2 | Zymbit’s security status LED |
| 11 | GND | System ground |
| 12 | PWR_BTN_IN | Replicates power button function of Pi 5 power button. Active low. |
- Tamper detection pins (pins 1, 3, 5): To close a tamper loop, PERIM0 is the TX and PERIM1/PERIM2 are the RX. So connecting PERIM0 to either of the RX lines completes the tamper for the associated loop. This is not simply a constant voltage, it is a pseudo random encoded sequence. Breaking this loop will trigger a tamper detection security event
- GPAUX pins (pins 4, 6): these are general purpose auxiliary pins passed through from the Zymbit HSM. These pins are currently reserved for future use
- 3V3 power (pin 8): This is the 3.3V power output that comes from the Raspberry Pi Compute Module
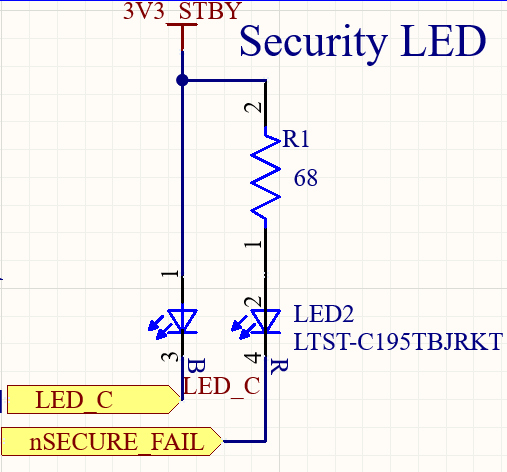
- Security indicator signals (pins 9, 10): These are typically used to drive LEDs which indicate the security status of the device. Note these pins are used together and typically drive a red/blue LED
- nSECURE_FAIL: indicates a security fault
- If there is a security fault but the LED_C2 is still active, this means a noncritical security failure. If the LED_C2 is not active at the same time this means a critical security fault and the system is not operational anymore
- LED_C2: Zymbit’s security status LED. When being used with the SCM4 or CM5 + Interposer, this will blink a pattern to give its status (see SCM LED Reference for details)
- nSECURE_FAIL: indicates a security fault
- Power button input (pin 12): This pin connects to the power button pin on the compute module after going through the HSM. Pull this pin low to activate.
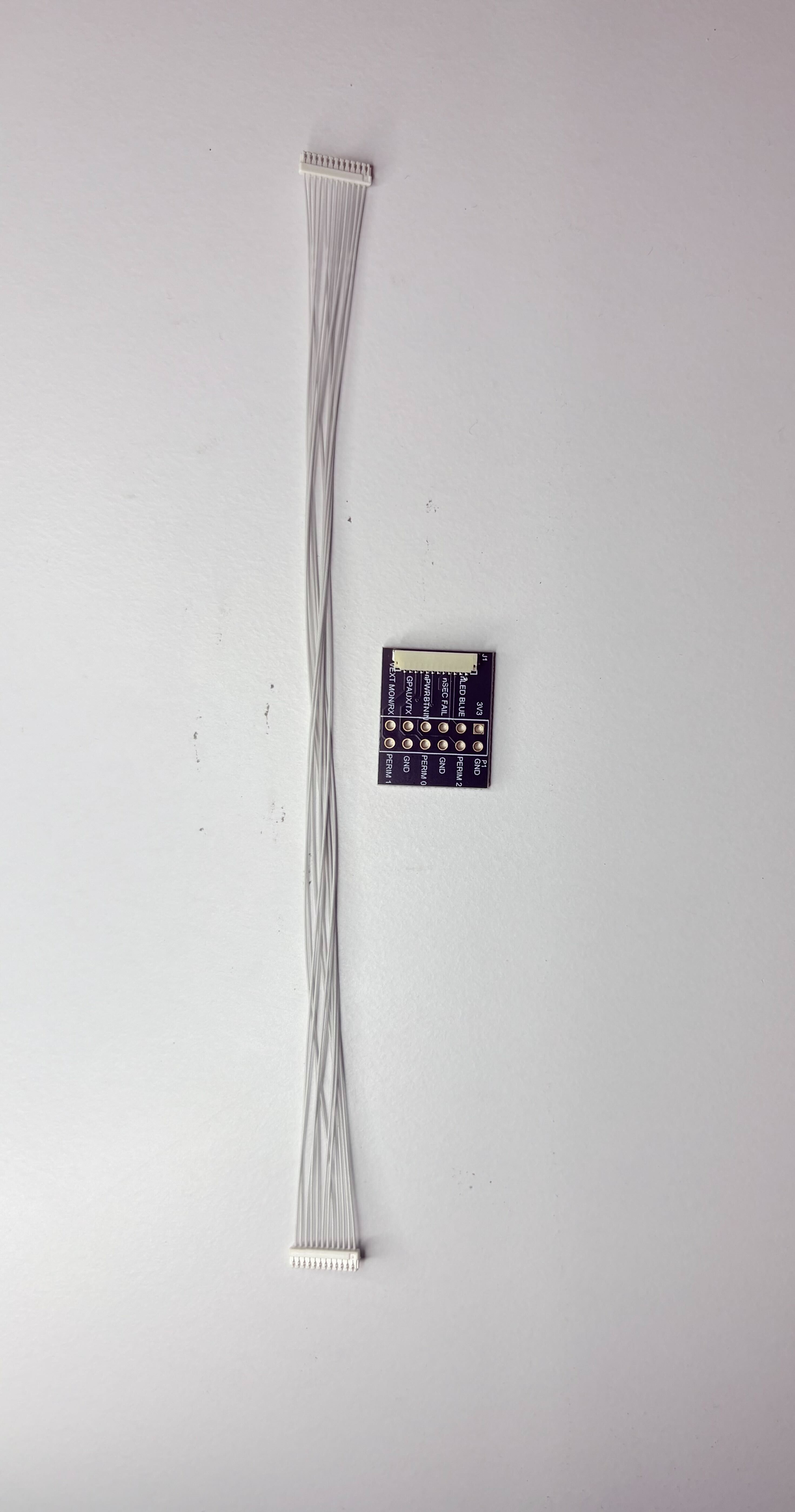
Breakout Board / Cable
Zymbit makes a breakout cable that exposes the pins of the Auxiliary connector (J1). Use one of the premade cable harnesses to connect to the breakout board. The pins are labeled according to their function and are laid out in a way that is intuitive for use, not in order of pin number! Use the pin descriptions above to identify how each pin operates.


Power on and confirm operation
Power up the Pi and you will see a blue LED blinking rapidly and consistently (5 blinks per second). This indicates the HSM is operational but not configured.
If the blue LED blinks erratically, or not at all, then there is an installation error and you should check your connections.